What is Single Intraday Coupling?
The aim of the Single Intraday Coupling (SIDC) is to create a single EU cross-zonal intraday electricity market. In simple terms, buyers and sellers of energy (market participants) are able to work together across Europe to trade electricity continuously on the day the energy is needed.
An integrated intraday market makes intraday trading more efficient across Europe by:
- promoting competition
- increasing liquidity
- making it easier to share energy generation resources
- making it easier for market participants to allow for unexpected changes in consumption and outages
As renewable intermittent production such as solar energy increases, market participants are becoming more interested in trading in the intraday markets. This is because it has become more challenging for market participants to be in balance (i.e. supplying the correct amount of energy) after the closing of the day-ahead market.
Being able to balance their positions until one hour before delivery time is beneficial for market participants and for the power systems alike by, among other things, reducing the need for reserves and associated costs while allowing enough time for carrying out system operation processes for ensuring system security.
The Evolution of SIDC and Its Geographical Scope
Single Intraday Coupling (SIDC) is a cooperation between Nominated Electricity Market Operators (NEMOs) and Transmission System Operators (TSOs) which enables continuous cross-border trading across Europe.
SIDC follows on from the XBID (Cross Border Intraday Project) which delivered, in June 2018, the first go-live of the intraday continuous trading platform. It allows energy networks to integrate via market coupling and to expand trading possibilities across Europe.
SIDC was launched on 12/13 June 2018 across 15 countries. In November 2019 SIDC went live in seven further countries and in September 2021 one additional country joined, resulting in 23 countries being coupled. In November 2022 the fourth go-live wave was achieved with 2 more countries. In total, as of today, 25 countries are coupled.
The table below lists the countries of the first, second, third, and fourth waves. SIDC is in line with the CACM (Capacity Allocation and Congestion Management) EU Target model for an integrated intraday market.
1 st wave June 2018
2 nd wave November 2019
3 rd wave September 2021
4 th wave November 2022
To accomplish SIDC, TSOs and NEMOs work in close collaboration.
Involved Parties
Transmission System Operators (TSOs):
50Hertz Transmission, ADMIE, Amprion, APG, AST, ČEPS, Creos, EirGrid, Elering, ELES, ELIA, ELSO, Energinet, ESO, Fingrid, HOPS, Litgrid, MAVIR, PSE, REE, REN, RTE, SEPS, SONI, Statnett, Svenska Kraftnät, TenneT DE, TenneT NL, Terna, Transelectrica and TransnetBW.
Nominated Electricity Market Operators (NEMOs):
BRM, BSP, CROPEX, EirGrid, EPEX SPOT, GME, HEnEx, HUPX, IBEX, Nord Pool, OKTE, OMIE, OPCOM, OTE, SONI, TGE, ETPA and BRM.
How Does the Single Intraday Coupling Work?
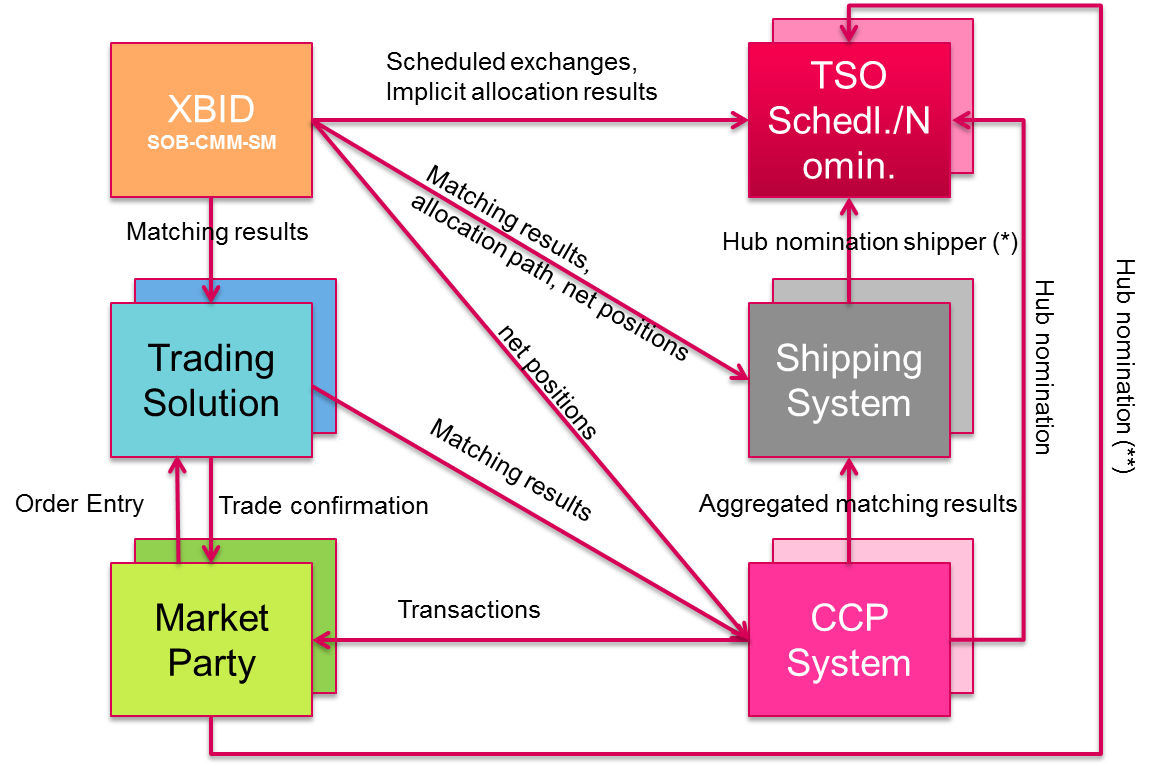
SIDC works on a common IT system with:
a Shared Order Book (SOB),
a Capacity Management Module (CMM), and
a Shipping Module (SM).
This means that orders entered by market participants for continuous matching in one country can be matched by orders submitted by market participants in any other country, as long as they are both within the project’s reach and transmission capacity is available.
The intraday solution supports continuous trading that is both:
explicit (capacity only - note: only provided where requested by National Regulatory Authorities (NRAs), i.e. at the French-German and the Croatian-Slovenian borders), and
implicit (capacity and energy together)
When market participants of each NEMO submit orders, they are put together in one Shared Order Book (SOB). In a similar way, TSOs make available all the intraday cross-border capacities in the Capacity Management Module (CMM).
This set-up allows NEMOs to operate their trading systems showing to market participants orders:
within the same NEMO
from other NEMOs in the same market area
from other market areas as long as there is enough capacity available
How Does the Single Intraday Coupling Work in Detail?
When a market participant submits an order for a different market area, it can be matched (i.e. met) as long as there is enough transmission capacity available. To match an order simply means that the market participant can meet and supply the energy demand.
Trade is concluded on a first-come-first-served principle where the highest buy price and the lowest sell price get served first.
Updating the SOB and CMM
When the order can be matched, the order matching is associated with implicit capacity allocation (this is when capacity and energy are priced together). While two orders are being matched, the SOB and CMM are updated immediately.
The update of the SOB means that the matched orders are removed from the SOB, and consequently the available transmission capacity in the CMM is updated. The number of borders that have their capacities updated depends on where the matched orders are located.
How Is Data About Trades Used?
The Shipping Module (SM) receives data from the SOB about all trades when they are concluded. These can be:
- between two different delivery areas, and
- in the same delivery area between two different NEMOs.
The Shipping Module (SM) of the SIDC solution provides information from concluded trades to all relevant parties such as NEMOs and TSOs.
The data from the SOB and the CMM is enhanced with data from:
- the relevant TSO,
- the Central Counter Party (CCP), and
- shipping agent data from the Shipping Module (SM).
This enhanced data is then sent to relevant parties such as the NEMOs and TSOs at the configured moments.

Future Development
The development of SIDC is a priority to all parties (NEMOs and TSO) involved in the project. Here we list future developments to expand and improve the efficiency of the SIDC.
Plans are underway to implement the functionality to address losses on HVDC cables.
SIDC has initiated the R&D phase for the implementation of flow-based allocation in continuous trading
Market Information
Products Available
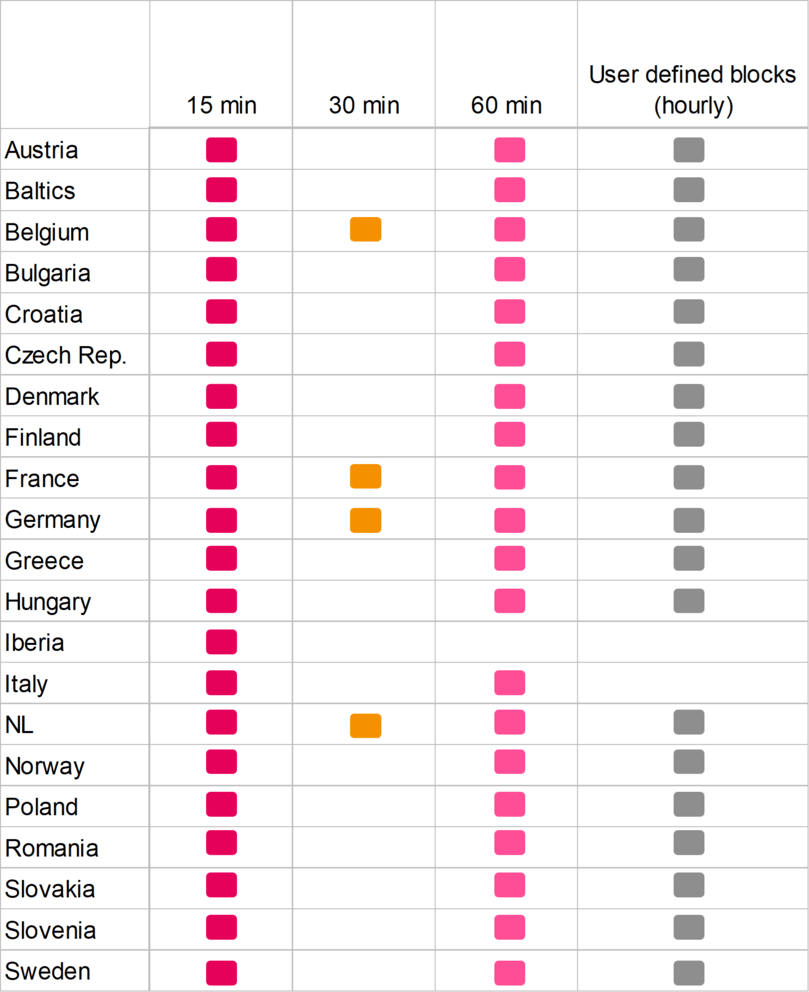
Available products by market are listed below.
- Size: minimum volume increment 0,1 MW
- Price tick: EUR 0,01/ MWh
- Volume range: from 0,1 MW to 999MW
- Price range: from -9999 EUR/MWh to 9999 EUR/MWh
15-min Products
15-minute products can be traded across all bidding zones, including internal and external bidding zone borders, with the following exception:
- The IT-GR and IT-SARD-IT CODC will remain at 60-minute MTU & OTU due to technical limitations of the HVDC cable.
30-min Products
- 30-min products are currently tradable across the borders FR-DE, DE-NL, DE-BE, FR-BE and BE-NL.
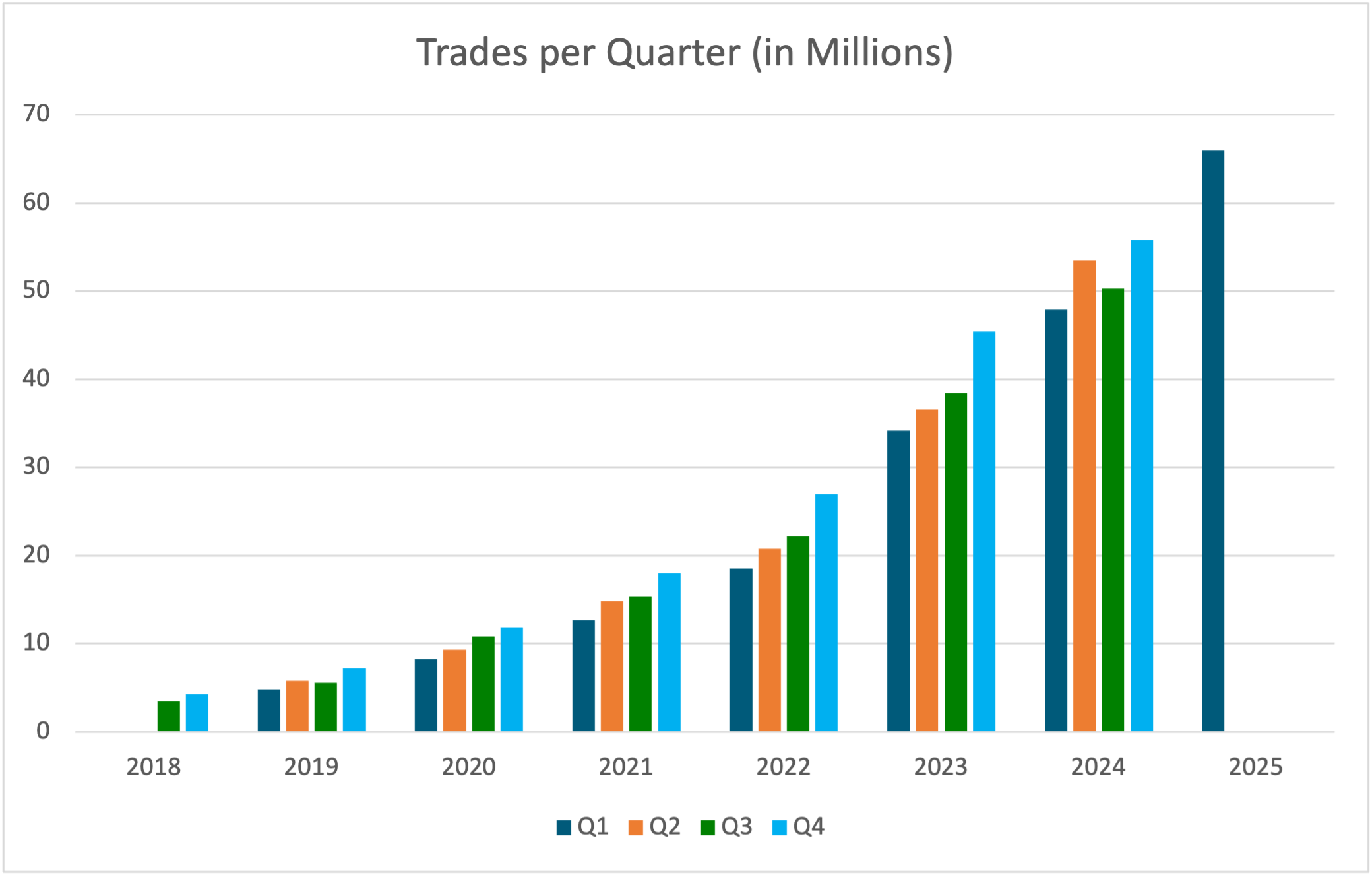
Number of Trades per Quarter (in Millions)
| Q1 | Q2 | Q3 | Q4 | |
|---|---|---|---|---|
| 2018 | 3,50 | 4,30 | ||
| 2019 | 4,80 | 5,80 | 5,60 | 7,20 |
| 2020 | 8,30 | 9,30 | 10,80 | 11,90 |
| 2021 | 12,70 | 14,90 | 15,40 | 18,00 |
| 2022 | 18,50 | 20,80 | 22,20 | 26,96 |
| 2023 | 34,22 | 36,58 | 38,47 | 45,41 |
| 2024 | 47,89 | 53,47 | 50,26 | 55,83 |
| 2025 | 65,93 | 73,26 |
Stakeholder Reports
To give stakeholders a comprehensive overview of the benefits SIDC delivers, the project has prepared reports featuring several indicators including amongst others traded volumes, average prices, cross-border capacity utilization, share of cross-bidding zone trades in overall volumes and availability of the SIDC platform. These reports cover the operational period since beginning of January 2019.
2025 Jan - Feb - Mar - Apr - May - Jun
2024 Jan - Feb - Mar - Apr - May - Jun - Jul - Aug - Sep - Oct - Nov - Dec
2023 Jan - Feb - Mar - Apr - May - Jun - Jul - Aug - Sep - Oct - Nov - Dec
2022 Jan - Feb - Mar - Apr - May - Jun - Jul - Aug - Sep - Oct - Nov - Dec
2021 Apr - May - Jun - Jul - Aug - Sep - Oct - Nov - Dec
2020 Q1/Q2 report - Q3/Q4 report
2019 Q1/Q2 report - Q3/Q4 report
Algorithm Monitoring
Pursuant to Article 8 of Annex I of ACER decision 04/2020 on the Algorithm methodology, SIDC has developed algorithm monitoring reports, which are generated on a monthly basis. These reports contain, amongst others, key indicators on the performance of the algorithm, prices, matched orders and volumes and the usage of SIDC products.
2025 Jan - Feb - Mar - Apr - May - Jun
2024 Jan - Feb - Mar - Apr - May - Jun - Jul - Aug - Sep - Oct - Nov - Dec
2023 Jan - Feb - Mar - Apr - May - Jun - Jul - Aug - Sep - Oct - Nov - Dec
2022 Jan - Feb - Mar - Apr - May - Jun - Jul - Aug - Sep - Oct - Nov - Dec
Cross‑Zonal Gate Closure Times Across Europe
The Intraday Cross‑Zonal Gate Closure Time (IDCZGCT) represents the last opportunity for market participants to get their cross‑border trades matched before electricity delivery begins. Under the Electricity Market Design Reform (EMDR), the aim is to harmonize intraday market timings across Europe by reducing the cross-zonal gate closure time from 60 minutes to 30 minutes.
This change improves alignment with actual generation operations, giving market participants greater flexibility to adjust their positions closer to real time. The shorter lead time also supports renewable integration, as market participants can refine their trading positions based on the latest generation forecasts. Overall, the 30‑minute timeline can also help reduce balancing costs by enabling more accurate and timely adjustments before delivery.
On 14 January 2026, the first window of European borders went live. The transition will continue gradually, with the remaining borders joining in over the next years. By 2029, most European borders are expected to apply the 30‑minute IDCZGCT. The latest status on the implementation is available in the “Border‑Based Overview for 30‑Minute IDCZGCT Derogations”, maintained on a regular basis.
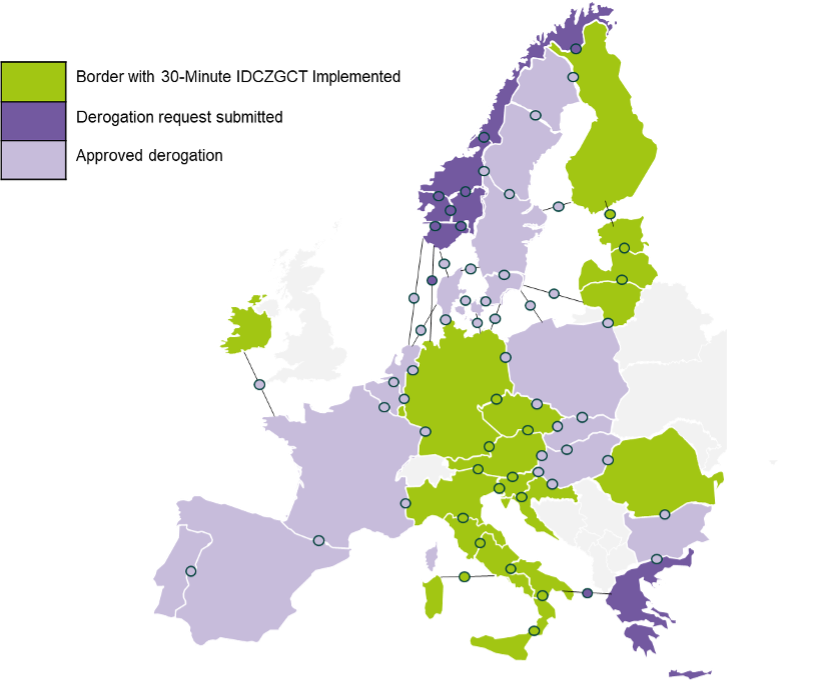
Statnett will submit derogation request officially to its NRA after transposition of relevant regulation.
IPTO has ongoing discussions with their local NRA, decision and publication expected by March 2026.
Derogation request not applicable on EE-FI border as 30-minute IDCZGCT is in effect prior to 01/2026.
Resources Available
Press Releases
2025
- Baltic Region - Successful Integration of European Power Exchange EPEX SPOT
- SIDC 15-Minute MTU Successful Implementation - Greece
- SIDC Press release on XBID incident on 6 September 2025
- SIDC Announces the Launch of 15-Minute Products in Several Further Bidding Zones and Bidding Zone Borders
2024
- SIDC Announces the Launch of 15-Minute Products in the Baltic Region
- SIDC announces the successful go-live for BRM in Romania
- SIDC announces the successful launch of 15-minute MTU capacity allocation on HR-SI and HR-HU borders
2023
- Successful test of 15-minute MTU allocation on HR-SI and HR-HU borders
- Successful go-live for ETPA as the third NEMO to operate in the Dutch Market Area within SIDC
- Confirmation of Go-Live date for ETPA
- Unsuccessful go-live for ETPA
- Confirmation of Go-Live date for ETPA as the third NEMO to operate in the Dutch Market Area within SIDC
2022
- SIDC Successful fourth wave go-live
- Expansion of 15-minute products to Bulgaria
- SIDC Fourth Wave Go-live Pre-Launch Event Agenda
- Fourth Wave Go-Live Pre-Launch Event
2021
- SIDC Successful Third Wave Go-Live
- SIDC Confirmation of the Go-Live Date for the Third Wave
- Revised Go-Live for SIDC Integration of Italy and New SIDC Release
2020
- Expansion of 30 and 15 minute products and Revised Local Implementation Project 14 Go-Live
- NEMOs and TSOs are safeguarding the Day-Ahead and Intraday market coupling
- Second Go-Live Impact
2019
- SIDC Successful Second Wave Go-Live
- SIDC Press Release Update on Second Wave Go-Live
- SIDC Confirmation of the Go-Live Date for the Second Wave
- XBID – 1st anniversary and announcement of the second Wave Go-Live
- Second Go-live impact
2018
Information Notes
- SIDC OPSCOM Report on the Critical Incident Experienced on 02/12/2025
- SIDC OPSCOM Report on the Critical Incidents Experienced From 25/11/2025 to 29/11/2025
- SIDC OPSCOM Report on the Critical Incident Experienced on 6th September 2025
- SIDC OPSCOM Report on Critical Incident Experienced on 24 January 2025
- SIDC OPSCOM Report on Automatic Partial Decoupling with Regards to the Intraday Auction (IDA1)
- SIDC Report on Critical Incident Experienced on 21st of May 2024"
- SIDC report on Critical Incident Experienced on 25th of July 2022
SIDC Joint Steering Committee Meeting Minutes
2022
2021
2020
- SIDC IDSC
- SIDC IDSC
- SIDC IDSC
- SIDC IDSC
- SIDC IDSC
- SIDC IDSC
- SIDC IDSC
- SIDC IDSC
- SIDC IDSC
- SIDC IDSC
- SIDC IDSC
2019
Intraday Operational Agreement
Publication of Intraday Operational Agreements according to article 20.7 of the Algorithm Methodology
The TSO Cooperation Agreement for Market Coupling (TCMC) can be found under the MCSC Webpage
According to article 20.7 of the Algorithm Methodology as approved by ACER all NEMOs shall in coordination with TSOs publish, by 1 September 2020, and then continuously update the relevant parts of the following documents:
- Operational contracts
- Operational procedures
- Change control procedures
- Monitoring procedures
- Fallback procedures
- Back-up procedures
Based on this regulatory requirement SIDC parties publish these documents for transparency purposes. Any consultation or use of these documents is at your own risk and responsibility and the parties to the SIDC cooperation cannot be held liable for any damage incurred as a result of the use of these documents. Furthermore, these documents can only be used or quoted provided prior written consent is obtained of the parties to the SIDC cooperation. No rights or obligations can be derived from these documents. The publication of these documents does not affect any (intellectual) property right pertaining to these documents or to the information contained therein. The publication of these documents does not preclude the rights of the parties to the SIDC cooperation to amend, replace or suppress the documents.
Please note the following:
For reasons of confidentiality certain parts of the content of the documents have been blackened out or have not been published (e.g. Exhibit 2, 13, 15 of the IDOA).
Exhibit 3 (Change Control Procedure), Exhibit 18 (OTH07-Algorithm monitoring procedure) and the related definitions in Exhibit 1 (Definition List) of the IDOA are to be adapted to reflect the relevant provisions of the Algorithm Methodology. For transparency reasons these documents are published subject to the reservation that they are still to be formally adopted by the parties to the SIDC cooperation via the signature of the Second IDOA Amendment.
Please note that for reasons of confidentiality certain parts of the content of the documents have been blackened out or have not been published (e.g. Exhibit 2, 13, 15 of the IDOA).
Intraday Operational Agreement (IDOA)
Exhibit 4: High Level Architecture (Including High Level Business Processes)
Exhibit 6: Operational Procedure see detailed list below
Exhibit 8: List of Operational Parties in SIDC/IDCT and SIDC/IDA
Exhibit 9: Non-Exhaustive List of Jointly Owned Developments
Exhibit 20: Statistical Data to Be Used for the Calculation of the Voting Share
Exhibit 21: List of Exhibits and Attachments to the IDA-CIP Services Contract
Exhibit 6: Operational Procedures
Normal Procedures
IDA_JOINT_NOR_03: Publication of ATCs (Including IDA Results)
IDA_JOINT_NOR_04: Delivery of Network Data from XBID CMM to IDA CIP Tool
IDA_JOINT_NOR_05: Delivery of Network Data from IDA CIP Tool to NEMOs IT Systems
IDA_JOINT_NOR_19: Generate & Send Program Authorizations and Transfer IDA Results
Back-Up Procedures
IDA_JOINT_BUP_03: Publication of ATCs (Including IDA Results)
IDA_BUP_04: Delivery of Network Data from XBID CMM to IDA CIP Tool
IDA_JOINT_BUP_05: Delivery of Network Data from IDA CIP Tool to NEMOs IT Systems
IDA_BUP_07: Send IDA Network Data to PMB and Cross-Check IDA Network Data
IDA_JOINT_BUP_19: Generate & Send Program Authorizations and Transfer IDA Results
Fallback Procedures
Exceptional Procedures
Configurational Procedures
Other Procedures
 ENTSO-E
ENTSO-E