The Internet was established to transfer files and share information between local area networks – there-fore it can be understood as the Internet of People. Until now, vast groups of the world’s citizens have had access to a more or less restricted World Wide Web. The IoT approach elaborates on the idea of connectivity not only for people but also technical devices and equipment. This kind of system allows data transfer and analysis without human-to-human and human-to-computer interactions. This approach has high potential for transportation, health care, manufacturing and smart buildings.
Technology Types
Within IoT, a set of hardware is used to communicate and interact with other devices in a controlled network. Hence, the communication part is of high importance, which can be wire-based or wireless.
Several communication standards are available currently:
- LTE or 5G for real-time applications within factories or autonomous mobility.
- Bluetooth for short length of transfer.
- Ethernet, ModBus, etc... for industrial applications.
Components & enablers
In general, the IoT architecture can be divided into three layers – the perception layer, network layer and application layer.
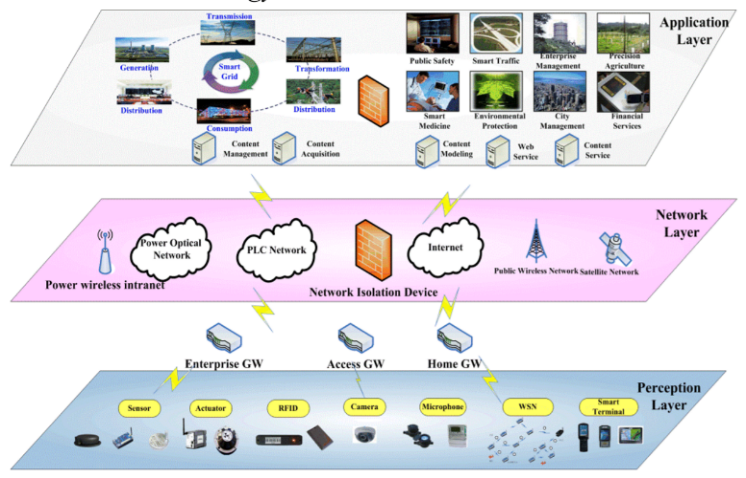
The major components in such a system are:
- Smart devices and sensors to gather data and transfer them
- Gateways to manage data traffic and adapt protocol
- Cloud storage to stack data
- Software solutions to analyse data and produce content out of derived information
- User interfaces to allow users to have access and control the network
Advantages & field of application
A system of interconnected physical objects and devices offers opportunities, e.g. to increase productivity in manufacturing or optimise power flow and consumption in heavy industries.
In power systems and grid infrastructure, a useful adaption must be discussed to evaluate best practices for a TSO’s core business.
Technology Readiness Level
TRL Score 7 – Prototype in demonstration
Research & Development
Several IoT solutions have already been introduced to the markets, provided by big companies such as IT or energy, but multiple small companies and start-ups are also involved in offering products for Power System Operators.
Best practice performance
Simple ‘IoT systems’ are already used in transmission systems nowadays to monitor and control their operation. More advanced IoT is now used in the Fingrid´s grid, where IBM´s IoT system Watson is used to increase the automation of the system. There are high expectations from application in distribution grids which have previously been passive, and IoT would allow them to implement distributed generation, DMS and other services, thereby increasing the efficiency, ecology and economy of such systems. This ranges from flow monitoring on the LV lines to consumption monitoring at the consumers´ side of the system. Such systems are already being researched by DSOs and other involved institutions.
Best practice application
References
N/A